12/02/2019 - Oliver Hagenlocher - Press
Production System by EMAG: Lightweight Rotor Shafts Machined with End-to-End Production Systems
A large number of studies are predicting rapid growth in e-mobility. The latest sales figures confirm the trend: According to the Center of Automotive Management, sales of electric cars in China and the USA increased dramatically last year. In Germany, the market share doubled at a low level. Mechanical engineering plays a central role by developing production technologies that enable safe and precise manufacturing of key components in the electric drive – in much larger quantities than previously needed. One example is the rotor shaft – this needs to transmit the high torque of an electric motor with precision and stability. At the same time, the combination of rotor laminations and shaft should be as light as possible to increase the electric vehicles range. So what is the most efficient way to produce a complex rotor shaft? The mechanical engineers at EMAG have been developing a variety of solutions for this, perfectly adapted to component geometry and production planning and ranging from fully automated production systems to customer-specific individual machines.
Lightweight construction has been one of the primary challenges in automotive engineering for decades. Each component, from gears to drive shafts to various housings, is expected to become lighter and smaller in order to reduce fuel consumption. Interestingly, the topic is becoming even more important in electric cars because less weight means covering longer distances without recharging. For this reason, the “range” issue will remain one of the primary objectives in e-mobility for the foreseeable future. In this context, massive and heavy electric motor shafts with relatively large laminated rotor cores do not fit the bill. EMAG is currently demonstrating how weight-optimized rotor shafts – and thus, weight-optimized electric motors in general – can be mass-produced. Their specialists for complete production systems have designed a line where soft machining, hardening and hard machining of a hollow (and therefore light) shaft take place one after the other. “All in all, the production of such a component is the perfect type of challenge for EMAG,” explains Peter Loetzner, President & CEO EMAG L.L.C. “We have all the necessary application know-how, ranging from turning, drilling and milling to hardening and grinding. We have also been developing the matching automation systems for decades. This means the complete line and process development all comes from a single source. We also supply customer-specific individual solutions for core sub-processes such as turning or grinding, which can be loaded by hand. These stand-alone machine installations can be the starting point for later expansion into a complete automatic line. In both cases, flexible modular solutions are used. From our various technology modules we configure tailor-made machines, allowing us to be prepared for any challenge.”
Assembled Shaft with Countless Advantages
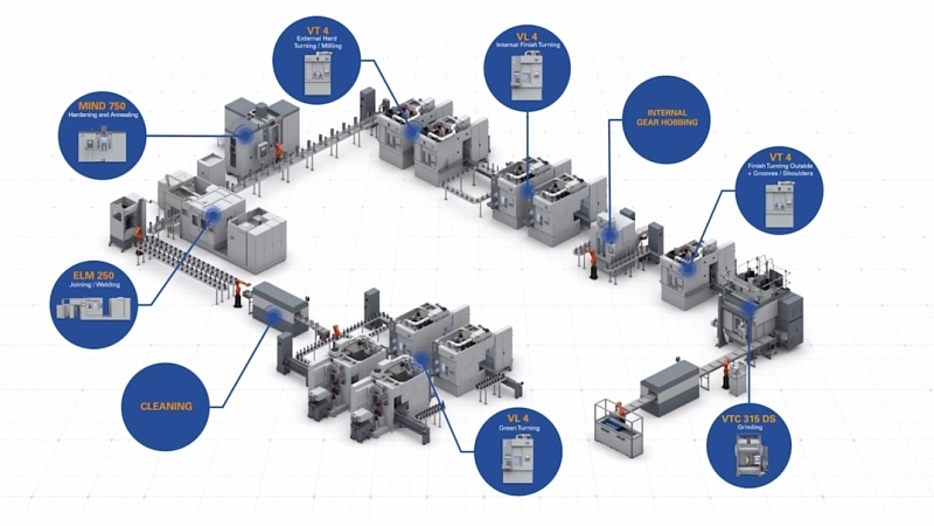
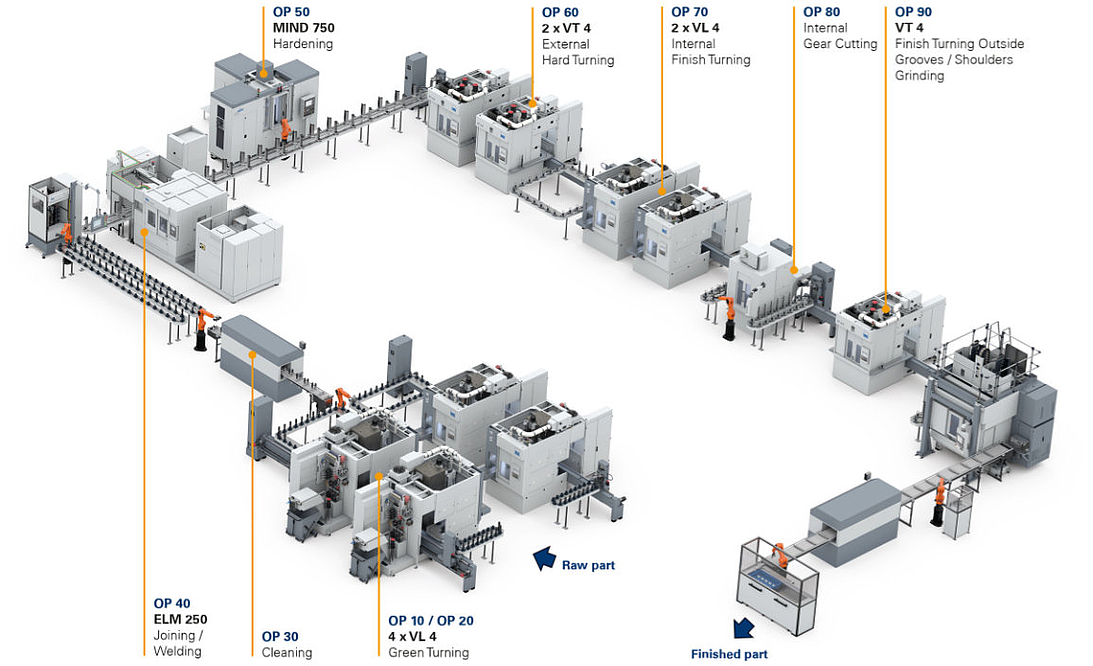
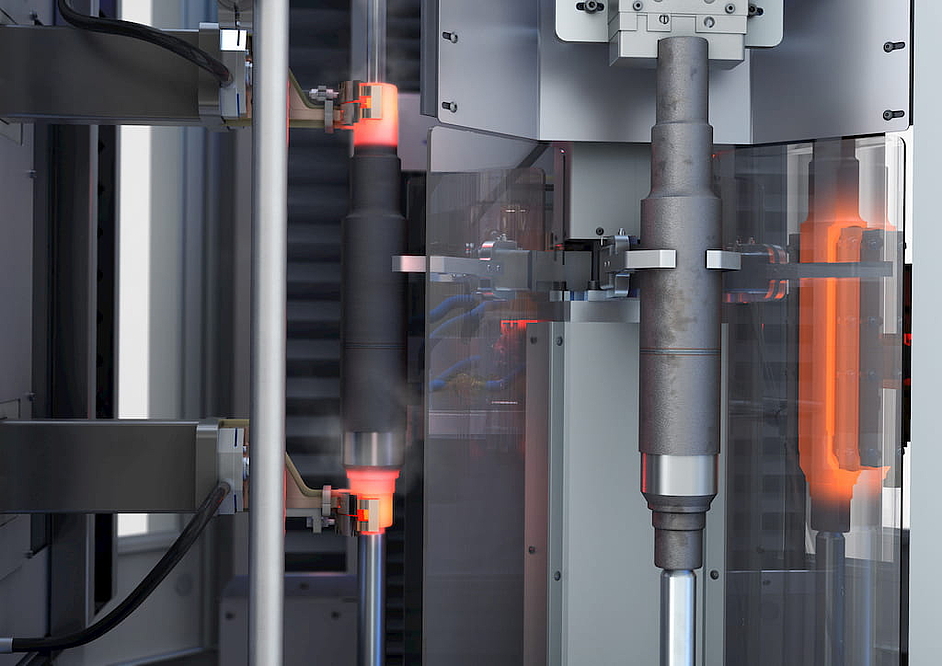
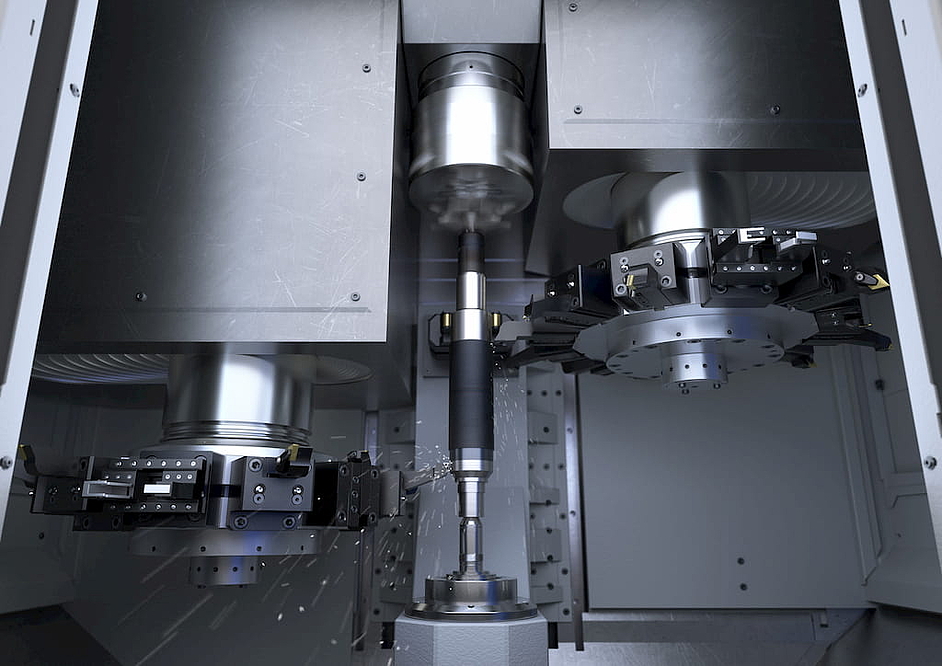
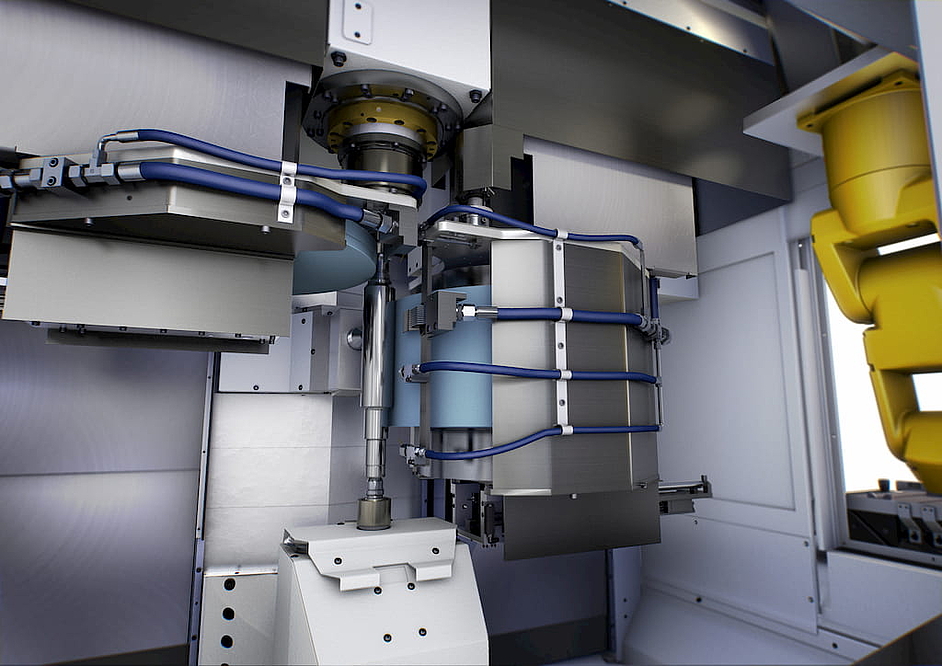
The "assembled" rotor shaft is an impressive example of this flexible approach. EMAG was asked to develop a multi-stage production system that would combine soft machining, laser welding, hardening and hard machining. In addition, the shaft is assembled during the process from two different end pieces – a basic principle that is known, for example, from assembled camshafts. The procedure can be broken down into short and partially parallel sub-processes - this approach often gives component developers more freedom. The shafts are finished with perfectly timed cycles: In the first two operations (10 and 20) the two different blanks are machined inside and outside, creating the hollow internal geometry. Four EMAG VL 4 pick-up machines are used for this. After a cleaning process (OP 30) the end pieces are joined together in an EMAG ELC 250 machine by laser welding (OP 40) – an extremely fast and safe process. The precisely controlled, concentrated energy of the laser beam allows high welding speeds and involves a minimum of distortions on the welded component. Next, the bearing seats are hardened in a matter of seconds and with high precision in the MIND 750 induction hardening machine by EMAG eldec (OP 50). Hard machining of the shaft starts with external turning in the EMAG VT 4-4 pick-up machine (OP 60) and internal turning in the modular VL series (OP 70). OP 80 and 90 consist of gear-cutting the shaft and finish-turning various shoulders on the outside. The finishing with close tolerances and high demands on surface quality is provided by the final grinding process on a vertical shaft grinding machine of the VTC series (OP 100).
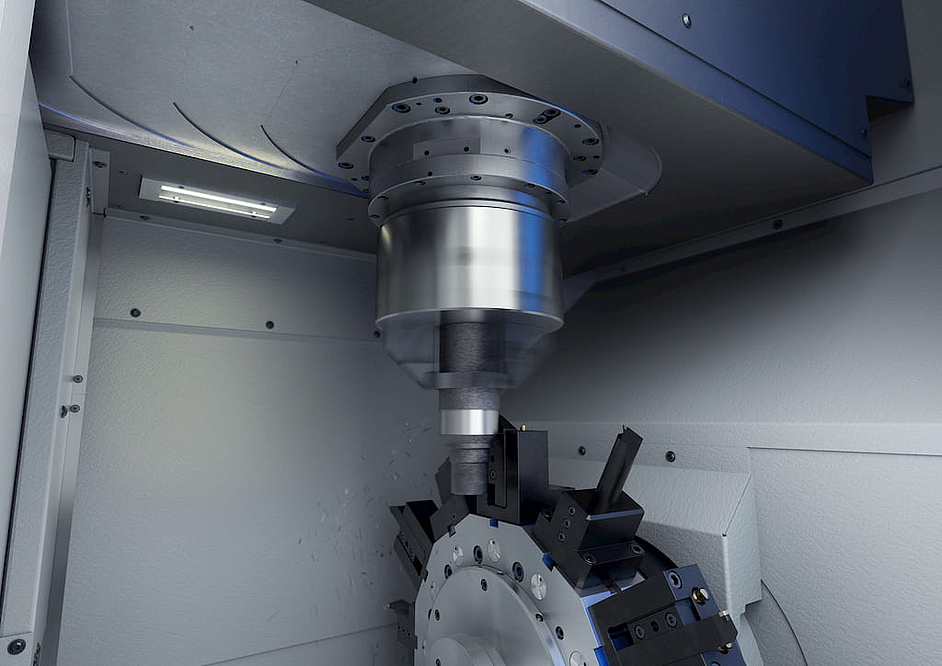
The shaft is then ready for joining with the corresponding laminations. The EMAG automation technology, which ensures transport between the machines, is adapted to customer requirements. For example, line gantries, stacking cells, accumulation conveyor belts or the EMAG proprietary TrackMotion system can be used. In any case, the system benefits from the standardization of all machines and their optimized interfaces. The customer benefits from a complete solution in the form of a comprehensive system and EMAG as the only contact needed during planning, implementation and service. In addition, the EMAG proprietary pick-up technology ensures speed in the process flow: The shaft (or its two separate components at the beginning) is transported into and out of the machining area with a movable workpiece spindle. The vertical turning and milling process is then performed at high cutting speeds with optimized chip flow.
Fast Solutions from a Single Source
About every 45 seconds a finished rotor shaft leaves this line. Unwanted idle times are reduced to a minimum. “The quality of such a production process is already determined at an early concept phase. EMAG uses its full range of expertise here – on the various tool applications, the design of multi-functional machine tools and their control and interlinking. The main objective is always to produce the best components – with the cycle time and quality that the customer is asking for. The customer ultimately decides whether this will be done in an integrated line with high annual volumes or, for example, with hand-loaded individual machines with smaller quantities and more flexibility,” concludes Peter Loetzner.
More information about Assembled Rotor Shafts for Weight-Optimized Electric Motors you will find here...
Images
Downloads
Contact

Oliver Hagenlocher
Area
Press and Communication